Evolution as defined is a gradual process of change in species. It was first introduced to us by Charles Darwin in the form of a hypothesis. He based this theory on the idea of natural selection of which it is the driving mechanism that allows desirable adaptation on certain individuals within a particular environment. These acquired traits were passed down to their offspring through what we now know as DNA through a process which we call as microevolution.

This Modern Synthesis explains how Genetics, with the emphasis to chromosomes, is linked to evolution process wherein traits are passed down from generation to generation.
Definition of Chromosome
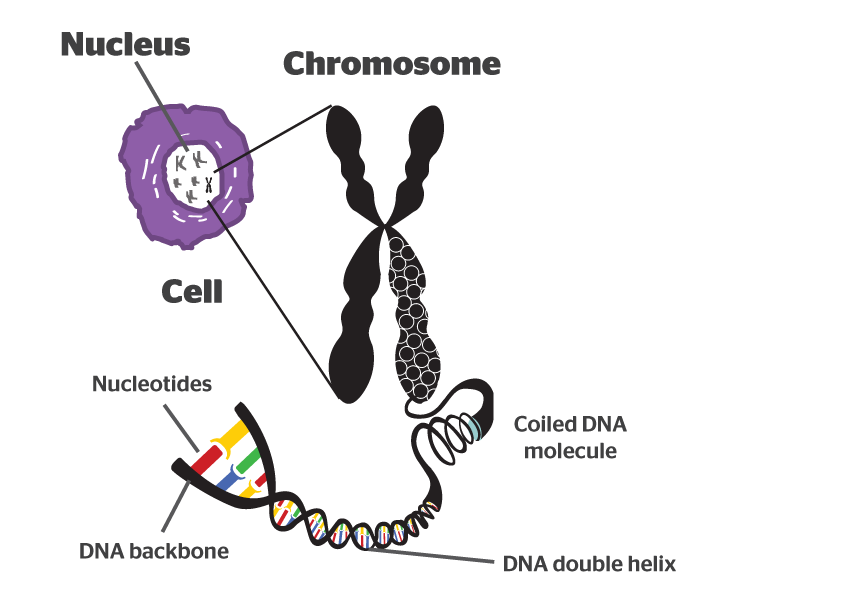
A chromosome is a unit of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that carries genes that code for proteins. When the said proteins are demonstrated, a set of observable characteristics known as phenotype, can be seen on a particular individual. Yet, a chromosome is still much more than just a mere unit or strand of DNA.
Structure
When a cell needs to divide due to a reason (or several reasons), it needs to make sure that the DNA which it bears will not be cut up and render the new cell useless. This is where chromosome takes action.
A chromosome is a concentrated form of DNA that ensures its safety during the process of cell division. The long strands of the DNA that coils around the core that bears the proteins called histones. Once the DNA is safely wrapped around the core, it then simply called a chromosome.
Chromosomes have two segments which are called sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are formed during the DNA replication and are identical to each other. They are bound together by the centrometer but will go into different cells during the division. This process makes sure that each cell bears the exact duplicate of the original cell and that it will function properly.
In sexual reproduction, chromosomes are arranged in homologous pairs of which one came from the organism’s father and the other from its mother. Bear in mind that these chromosomes hold the information for the same traits and the combination of both. These also determine what phenotype an offspring will demonstrate in the future.
Relation with Evolution
Chromosomes bear the information of evolution within the bounds of diminutive eukaryotic cells that get passed through from parent to offspring. The absence of chromosomes will simply mean that the transfer of genetic information from one generation to another is impossible.